Django:Introduction 20cs023,27,30
What is Django?
Django is a Python framework that makes it easier to create websites using Python.
Django takes care of the difficult stuff so that you can concentrate on building your web applications.
Django emphasizes the reusability of components, also referred to as DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself), and comes with ready-to-use features like a login system, database connection, and CRUD operations (Create Read Update Delete).
How does Django Work?
Django follows the MVT design pattern (Model View Template).
- Model - The data you want to present, usual data from a database.
- View - A request handler that returns the relevant template and content - based on the request from the user.
- Template - A text file (like an HTML file) containing the web page's layout, with logic on how to display the data.
Django Requires Python
To check if your system has Python installed, run this command in the command prompt:
python --versionIf Python is installed, you will get a result with the version number, like this
Python 3.9.2PIP
To install Django, you must use a package manager like PIP, which is included in Python from version 3.4.
To check if your system has PIP installed, run this command in the command prompt:
pip --versionIf PIP is installed, you will get a result with the version number.
For me, on a windows machine, the result looks like this:
pip 20.2.3 from c:\python39\lib\site-packages\pip (python 3.9)Virtual Environment
It is suggested to have a dedicated virtual environment for each Django project, and one way to manage a virtual environment is venv, which is included in Python.
With venv, you can create a virtual environment by typing this in the command prompt, remember to navigate to where you want to create your project:
Windows:
py -m venv myprojectThis will set up a virtual environment, and create a folder named "myproject" with subfolders and files, like this:
myproject
Include
Lib
Scripts
pyvenv.cfgThen you have to activate the environment, by typing this command:
Windows:
myproject\Scripts\activate.batOnce the environment is activated, you will see this result in the command prompt:
Install Django
Finally, we can install Django.
Remember to install Django while you are in the virtual environment!
Django is installed using pip, with this command:
Windows:
(myproject) C:\Users\Your Name>py -m pip install DjangoCheck Django Version
You can check if Django is installed by asking for its version number like this:
(myproject) C:\Users\Your Name>django-admin --versionIf Django is installed, you will get a result with the version number:
My First Project
Once you have come up with a suitable name for your Django project, like mine: myworld, navigate to where in the file system you want to store the code (in the virtual environment), and run this command in the command prompt:
django-admin startproject myworldDjango creates a myworld folder on my computer, with this content:
myworld
manage.py
myworld/
__init__.py
asgi.py
settings.py
urls.py
wsgi.pyRun the Django Project
Now that you have a Django project, you can run it, and see what it looks like in a browser.
Navigate to the /myworld folder and execute this command in the command prompt:
py manage.py runserverWhat is an App?
An app is a web application that has a specific meaning in your project, like a home page, a contact form, or a members database.
In this tutorial we will create an app that allows us to list and register members in a database.
But first, let's just create a simple Django app that displays "Hello World!".
Create App
I will name my app members.
Start by navigating to the selected location where you want to store the app, and run the command below.
If the server is still running, and you are not able to write commands, press [CTRL] [BREAK] to stop the server and you should be back in the virtual environment.
py manage.py startapp membersDjango creates a folder named members in my project, with this content:
myworld
manage.py
myworld/
members/
migrations/
__init__.py
__init__.py
admin.py
apps.py
models.py
tests.py
views.py
These are all files and folders with a specific meaning.
Views
Django views are Python functions that takes http requests and returns http response, like HTML documents.
A web page that uses Django is full of views with different tasks and missions.
Views are usually put in a file called views.py located on your app's folder.
There is a views.py in your members folder that looks like this:
members/views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.Find it and open it, and replace the content with this:
members/views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world!")This is a simple example on how to send a response back to the browser.
But how can we execute the view? Well, we must call the view via a URL.
URLs
Create a file named urls.py in the same folder as the views.py file, and type this code in it:
members/urls.py:
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name='index'),
]
The urls.py file you just created is specific for the members application. We have to do some routing in the root directory myworld as well. This may seem complicated, but for now, just follow the instructions below.
There is a file called urls.py on the myworld folder, open that file and add the include module in the import statement, and also add a path() function in the urlpatterns[] list, with arguments that will route users that comes in via 127.0.0.1:8000/members/.
Then your file will look like this:
myworld/urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path('members/', include('members.urls')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]If the server is not running, navigate to the /myworld folder and execute this command in the command prompt:
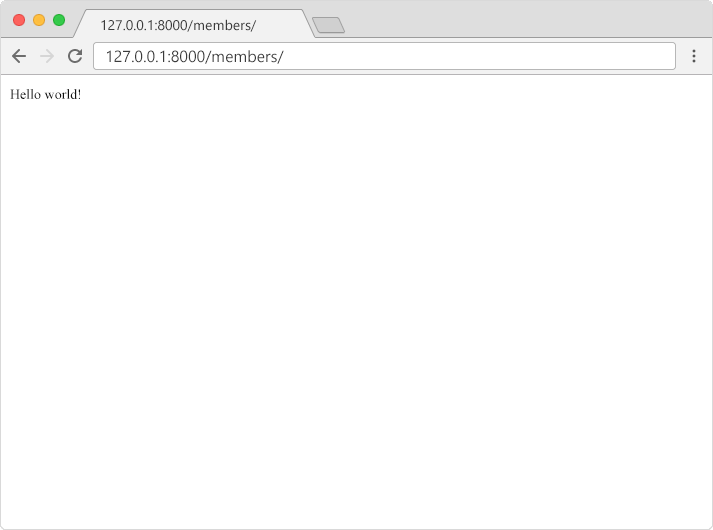
py manage.py runserverIn the browser window, type 127.0.0.1:8000/members/ in the address bar.
Created By 20CS023,20CS027,20CS030 :)





Comments
Post a Comment